Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical manipulation that allows the accurate diagnosis of knee diseases by helping the real-time examination of the intra-articular structures and a variety of therapeutic surgical manipulations in the knee cavity.
Arthroscopy of the knee joint helps
-
to specify the diagnosis;
-
to take material for research;
-
to resolve the issue of the necessity and method for the surgery;
-
to determine the exact location of the pathological focus.
What are the indicators that an arthroscopy is the best option?
The indications that arthroscopy of the knee joint might be the best option can be divided into two groups: the diagnosis and treatment of the articular pathology.
Indications for arthroscopy are:
Indications of the need for arthroscopy are: the need to diagnose the knee articular pathology between traumatic, degenerative-dystrophic, inflammatory, autoimmune, or rheumatological types of injury. The necessity for biopsy of the joint capsule. Traumatic damages in the knee menisci. Injuries of the intra-articular ligament, especially of the anterior and posterior cruciate ligament(s). Arthroscopic sanitation of the knee i.e. the elimination of pus, blood, serous effusion from the joint cavity and the introduction of antiseptics and antibiotics to eliminate the inflammation is also possible. Another option is the need to diagnose and treat deforming osteoarthritis in the knee joint.
The treatment of a recurrent dislocation of the patella. The elimination of loose elements in the joint cavity, e.g. bone fragments in fractures, osteophytes, blood clots or any other item that can cause acute blockades of the knee joint. Excision of a damaged area of the hyaline cartilage. Diagnosis and treatment of the intra-articular fractures of the bones. Restoration of the joint junction in the rheumatoid arthritis. Diagnosis of tumors of the knee joint.
What are the contraindications of arthroscopy?
-
Contraindications to anesthesia. For example, a severe general state of the patient or intolerance to certain anesthetics due to the allergies.
-
Acute and chronic diseases of the knee joint. And also exacerbation of inflammatory phenomena in the knee joint.
-
Adhesive process in the joint cavity.
-
Contracture of the joint. Limitation of its mobility due to the muscle spasm, sclerosis of ligaments, etc.
-
Bone and pseudo ankylosis
-
Infected wound.
-
Purulent inflammation in the tissues around the joint, the joint can be infected at that.
-
The general severe state of the patient, when any surgical interventions are contraindicated.
-
Extensive damage, when the ligaments and articular capsule are broken, the joint tightness is broken. Because of this, the surgeon will not be able to stretch the articular cavity with the liquid so that it can be properly examined.
-
Massive hemorrhage to the joint, continuing bleeding. Blood in the joint cavity does not allow to examine the intra-articular structures.
Your Journey
A personal assistant supplied by Remed Assistance will welcome you at the airport, accompany you to the hospital and do the necessary translation in order to guarantee a worry-free medical trip experience in Turkey.
Planning the arthroscopic surgery
Despite the minimal traumatism for the body, the arthroscopic surgery on the knee joint requires preparation, as it relates to the surgical interventions, albeit the insignificant ones.
The patient submits all necessary tests, consults the highly specialized doctor and obtains some types of examination. All this happens, as a rule, on an outpatient basis. Sometimes, on request of the patient, they can be hospitalized some 1-2 days before the surgery for the preoperative diagnosis. By the consultation the patient should have the results of an X-ray and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the knee joint.
Preparation for arthroscopy obligatory includes:
-
blood and urine tests, coagulogram (blood coagulability studies);
-
chest x-ray;
-
electrocardiography;
-
consultation with the therapist;
-
consultation with the anesthesiologist;
-
the whole complex of the diagnostic examinations related to the main pathology.
Steps of the Operation
As a rule, the duration of arthroscopy does not exceed 1 hour, but everything depends on the purpose of the procedure. Anesthesia can be of two types: spinal (epidural) anesthesia is used more often; sometimes it can be general anesthesia.
After treating the skin with an antiseptic, a small incision is made and an arthroscope is inserted into it. Then a special sterile liquid is injected to make the joint swell, and all its structural parts become better visible in the arthroscope. After an accurate detection of the problem, separate small incisions are made for the surgical instruments with which the surgery is performed.
The following surgery types are performed on the knee joint:
-
resection of the meniscus
-
stitching the meniscus
-
removal of the meniscus cyst
-
anterior cruciate ligament plasty
-
posterior cruciate ligament plasty
-
revision plasty of the anterior cruciate ligament
-
revision plasty of the posterior cruciate ligament
-
medial collateral ligament plasty
-
lateral collateral ligament plasty
-
removal of free chondromic bodies
-
resection of the damaged cartilage (shaving / ablation)
-
microfracturing (tunneling) of the damaged cartilage area
-
re-fixation of the cartilage at fibering osteochondritis
-
cartilage autotransplantation (OATS)
-
surgery at the recurrent patellar dislocation: lateral capsule release, Yamamoto surgery, medial capsuloraphy, reconstruction of MPFL, transposition of tuberosity of the tibia.
-
osteosynthesis with intra-articular fractures of the femur and tibia
-
arthroscopic arthrolysis of the knee joint
After completion of all necessary manipulations in the joint cavity the fluid is pumped back, tools are removed, antiseptics and antibiotics are introduced into the joint cavity to prevent infection, and the incisions are closed with a large soft bandage over the sutures or with small striae patches.
Recovery and rehabilitation
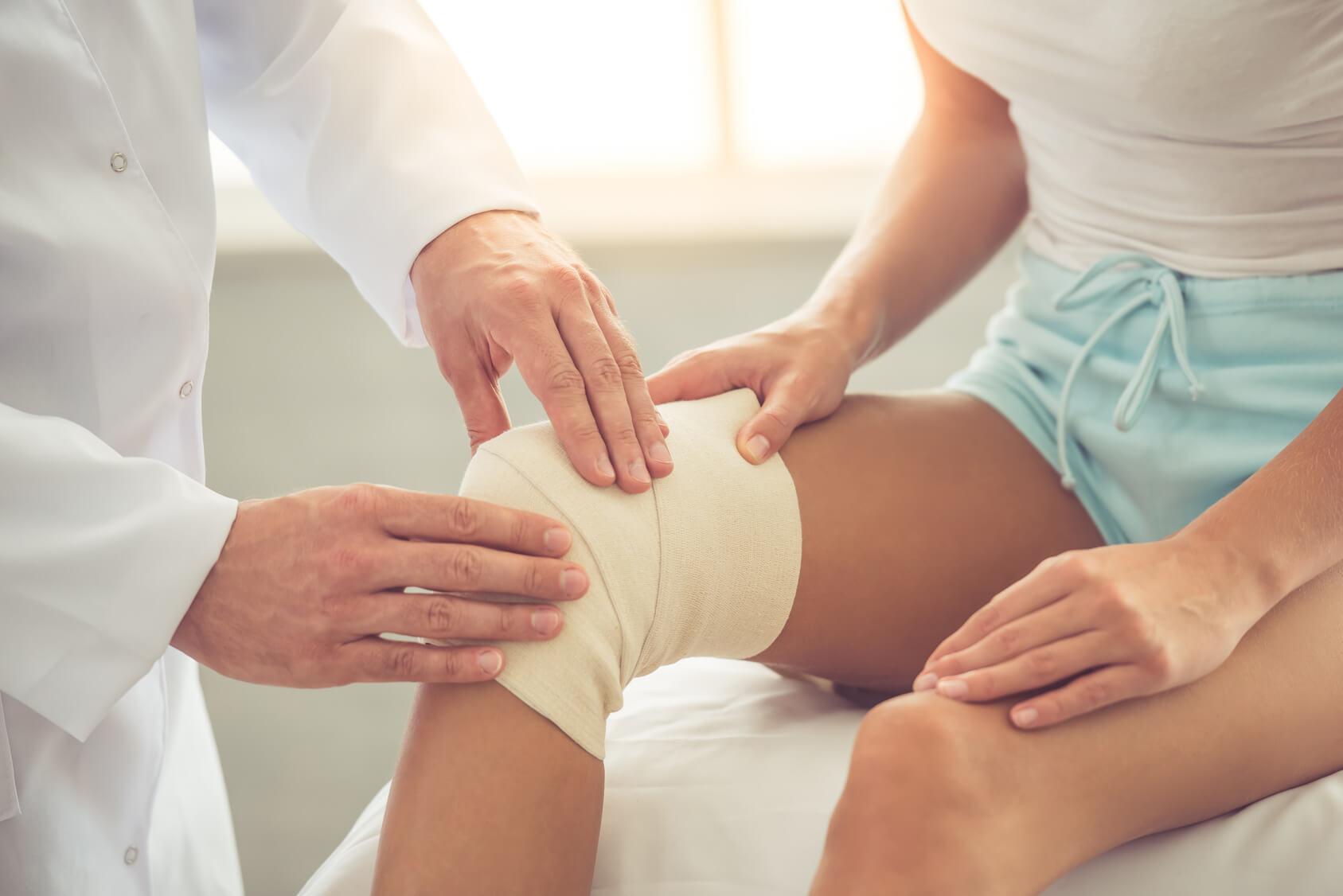
Rehabilitation after the arthroscopy begins immediately after the surgery is over. A pressure bandage is applied on the knee to prevent hemorrhage into the joint cavity (hemarthrosis) and swelling, an elevated position for the limb to be provided, and the cold is applied locally. Duration of stay in the hospital is 1-2 days, if necessary, the painkillers to be prescribed during this period.
The patient is recommended some physical exercise under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
Departure from airport
You will be accompanied to the airport by a personal assistance. If necessary wheelchair assistance will be arranged in the airport. By provided flight authorization and medical report, you will take your flight to home
Follow up
After your return, Remedhealth.com agents will be available for any future request.
